gravimetric method blood loss|Optimal Estimated Blood Loss Major Surgery : convenience store Our study assesses the accuracy of intraoperative blood loss measurement using the Triton system and those methods that are used mostly in clinical practice, especially the . WEBEnter your address to see if Poke Poke delivery is available to your location in Toronto. How do I order Poke Poke delivery online in Toronto? There are 2 ways to place an .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 11 linhas · O calendário completo de 2024 da UFC na ESPN (BR).
The gravimetric method considers external blood loss. Frequently used conversion in literature “1 g equals 1 ml of blood” is only an approximation. Blood, depending on the current Hct, does not have the same density as water. Both lead to measurement inaccuracies.The gravimetric method of weighing surgical sponges is used to quantify intraoperative blood loss. The dry mass minus the wet mass of the gauze equals the volume of blood lost. This . Our study assesses the accuracy of intraoperative blood loss measurement using the Triton system and those methods that are used mostly in clinical practice, especially the . It describes the primary methods for determining blood loss, including visual assessment, photometric analysis, gravimetric blood loss determination, blood loss formulas .
In this study, we analysed the estimation of blood loss during the intraoperative period in major orthopaedic surgery (total hip arthroplasty and hip prosthesis replacement) . Methods for measuring blood loss are often complex, vague or difficult to implement in clinical practice, and they tend to differ across institutions, disciplines and among individual health care providers. . Gravimetric: .
The aim of the study is to compare several methods of blood loss quantification—visual estimation by a surgeon and an anesthesiologist, gravimetric method, .
The most popular technique is subjective visual estimation, followed by formula-based estimation, gravimetric-based estimation, and a novel approach that uses facial .The bias for estimated blood loss (ml) was lowest for colorimetric methods (57.59 95% CI 23.88-91.3) compared to the reference, followed by gravimetric (326.36 95% CI 201.65-450.86) and . The gravimetric estimation of blood loss during surgery correlated with actual estimated blood loss and should be considered in the routine estimation ofBlood loss during Surgery. Background: Estimation of blood loss during surgery is a critical component that may affect patients’ management. Objective: The study evaluated the accuracy of the gravimetric .One 2022 study evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of the gravimetric method (i.e. weighing all blood-soaked laparotomy sponges and blood collected in suction canisters to determine the amount of blood loss) against spectrophotometry to determine the amount of Hb extracted from the sponges and canisters . Compared to spectrophotometry, the .
Total blood loss was calculated using gravimetric method and was compared to value given by visual estimation. Furthermore, comparison was done between the visual estimation values of the attending obstetrician and the obstetric nurse. Results: Obstetrician observed 21.47% less blood loss than the actual (by gravimetric method) blood loss. Blood loss during major abdominal surgery is an essential parameter in the evaluation of strategies aimed at reducing perioperative bleeding. However, blood loss quantification remains unreliable and inaccurate. The aim of this study was to compare several methods of blood loss quantification—visual estimation by surgeon and anesthesiologist, the .The gravimetric method of determining blood loss requires weighing surgical sponges before and after use. The difference in weight is assumed to be the volume of blood lost as measured in milliliters. This assessment is based upon density which is defined as mass per unit volume. Water density is dependent upon temperature.Purpose. The gravimetric method of weighing surgical sponges is used to quantify intraoperative blood loss. The dry mass minus the wet mass of the gauze equals the volume of blood lost. This method assumes that the density of blood is equivalent to water (1 gm/mL). This study's purpose was to valida .
Gravimetric analysis describes a set of methods used in analytical chemistry for the quantitative determination of an analyte (the ion being analyzed) based on its mass. The principle of this type of analysis is that once an ion's mass has been determined as a unique compound, that known measurement can then be used to determine the same analyte's mass in a mixture, as long as .
Background: Blood loss during major abdominal surgery is an essential parameter in the evaluation of strategies aimed at reducing perioperative bleeding. However, blood loss quantification remains unreliable and inaccurate. The aim of this study was to compare several methods of blood loss quantification-visual estimation by surgeon and anesthesiologist, the . The original study compared visually estimated blood loss, gravimetric QBL, and a colorimetric blood loss estimation to a reference hemoglobin extraction assay during scheduled cesarean delivery. . In 37 cases (74%), there was concordance among both methods that the blood loss was less than 1,000 mL. These relationships are illustrated in .Purpose: Among various methods for estimating blood loss, the gravimetric method is the most accurate; however, its use in routine practice is complicated. Although several equations have been proposed for this purpose, there is no consensus on the most suitable. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in seven secondary and tertiary hospitals between March .The accuracy of the gravimetric method was confirmed in simulated postpartum haemorrhage. The clinical study shows that gravimetric measurement of blood loss is correlated with the fall in haemoglobin in postpartum haemorrhage where blood loss exceeds 1500mL. The method is simple to perform, require .
Background In clinical practice, postpartum blood loss is usually estimated visually. Studies have demonstrated visual estimation of blood loss is inaccurate in comparison to other methods, but little attention has been given to gravimetric measurement (weighing). Objective To determine the difference between gravimetric measurement of blood loss (MBL) and visual estimation .Objective: To compare gravimetric and colorimetric methods of quantifying surgical blood loss, and to determine if there is a correlation between preoperative hemostatic tests (buccal mucosa bleeding time [BMBT] and intraoperative blood loss). Study design: Prospective clinical study. Animals: Dogs (n=15) admitted for cutaneous tumor excision, orthopedic procedure, or . The gravimetric method is an indirect measurement of blood loss that is calculated by summing up the differences in weight of operating room materials before and after contamination with blood and/or fluid.Gravimetric methods have also been reported. Lee et al.2 compared gravimetric and laboratory methods of quantifying blood loss during animal surgery. Intraoperative blood loss was first quantified by measuring irrigation fluid and the weight of surgical sponges. Blood loss was determined as the weight
Measures of surgical sponge estimated blood loss (EBL) from the Triton system were compared with the estimates of blood loss via the gravimetric method and photometric analysis which were processed as the following. After the images were scanned by the application, operative sponges were transported to a medical waste room for further assessment. Objective In view of the current clinical inaccuracies and underestimations of postpartum hemorrhage amount, this study aims to investigate the incidence, etiology, clinical characteristics of postpartum .
There are many methods for intraoperative blood loss estimation, e.g., gravimetric, photometry, and visual estimation, but the most used method is visual estimation. . or time consumption, e.g., gravimetric method, as the gauze must be weighed pre- and post-use (1, 5). Although visual estimation is a commonly used method, it is the least .
A randomized controlled trial in India demonstrated the superiority of the volumetric approach over the gravimetric method for detecting blood loss exceeding 500 mL (Ambardekar et al., 2014). However, few studies have compared the difference between the volumetric method with gravimetric method in terms of adverse outcomes of PPH, and .
Estimating intraoperative blood loss is one of the daily challenges for clinicians. . by gravimetric (0.77 95% CI 0.61-0.93) and finally visual methods (0.61 95% CI 0.40-0.82). The bias for estimated blood loss (ml) was lowest for colorimetric methods (57.59 95% CI 23.88-91.3) compared to the reference, followed by gravimetric (326.36 95% CI .
Objective This study aims to compare the accuracy of visual, quantitative gravimetric, and colorimetric methods used to determine blood loss during cesarean delivery procedures employing a hemoglobin extraction assay as the reference standard.Study Design In 50 patients having cesarean deliveries blood loss determined by assays of hemoglobin content on . A total of 46 publications are included in this review. The methods used to measure blood loss are categorized into visual estimation, direct measurement, gravimetric, photometry, and miscellaneous. Methods are described and compared. A combination of direct measurement and gravimetric methods are the most practical.
We found no statistically significant correlation between the amount of blood loss estimated by the gravimetric method and the actual blood loss as measured by the colorimetric method (P = 0.074).
how hard is the miller analogies test
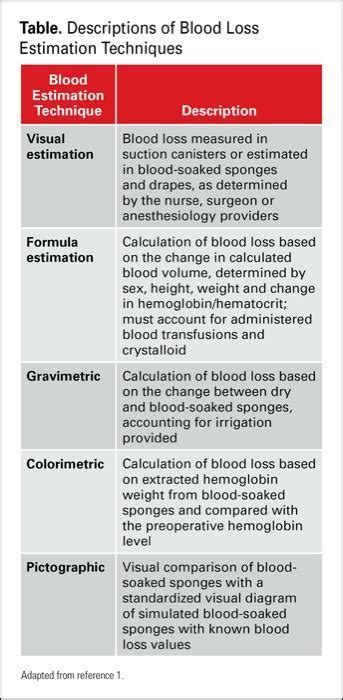
[19][20][21] The gold standard approach to blood loss measurement is to use a gravimetric method 22, 23 ; however, gravimetric measurement of blood loss is time-consuming and difficult to apply in . The aim of this integrative review was to evaluate the various methods of assessing maternal blood loss during childbirth. A systematic, integrative review of published research studies was conducted. . The gravimetric method was used to assess the accuracy of visual estimation in 150 vaginal births and found that visually estimated blood . The bias for estimated blood loss (ml) was lowest for colorimetric methods (57.59 95% CI 23.88–91.3) compared to the reference, followed by gravimetric (326.36 95% CI 201.65–450.86) and visual . Purpose. The gravimetric method of weighing surgical sponges is used to quantify intraoperative blood loss. The dry mass minus the wet mass of the gauze equals the volume of blood lost.
Optimal Estimated Blood Loss Major Surgery
Measurement of Intraoperative Blood Loss in Pediatric
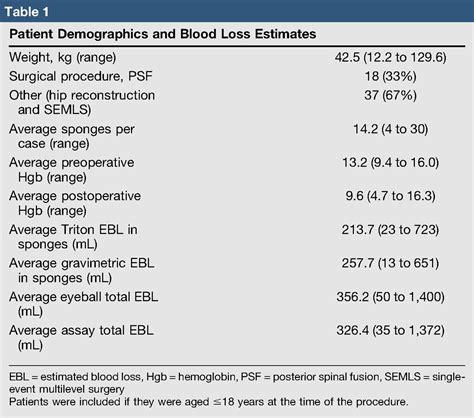
Resultado da Is Seriously Red (2022) streaming on Netflix, Disney+, Hulu, Amazon Prime Video, HBO Max, Peacock, or 50+ other streaming services? Find out where you can buy, rent, or .
gravimetric method blood loss|Optimal Estimated Blood Loss Major Surgery